The Bank of Japan has started a demonstration experiment of the "digital yen", and the central bank is considering a digital currency - what is the difference from electronic money?
close table of contents
Cashless payment spreads rapidly
Although there are regional differences, the use of cashless payment services has spread. In urban areas, not only credit cards but also many stores accept QR code payments. I use credit card payment for online shopping, and my salary is also bank transfer. Less cash handling. When using toll roads, all you have to do now is pay ETC.
In areas with well-developed public transportation, FeliCa-based electronic money can be used as a matter of course. There are various forms of electronic money, including not only IC cards and smartphones, but also smartwatches. Even the ring-shaped 'EVERING' has appeared and is attracting attention.
Because of this situation, we use cashless payment in various situations in our business. If cashless payment is made in business, there is no need to submit paper receipts at the time of expense reimbursement if the conditions are met, and it is possible to pay out to an electronic money account.
In addition, it seems that the payment of salaries will be cashless. There is a possibility that the ban on "wage payment by digital money", which pays to registered accounts for electronic money and QR code payments, will be lifted in 2021.
Will cash just go unused?
Ideas for digitizing fiat currencies
Fiat currencies such as the yen, dollar, and euro are issued by the central banks of countries. In an age when cashless payment technology has advanced so much, the idea of issuing digital data instead of physical banknotes and coins naturally arose. It is a concept called "Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)".
Requirements for Central Bank Digital Currencies
Digital currencies are electronic data that can be used for transactions in place of cash. It is similar to electronic money, but the required functions and reliability are different. According to the Bank of Japan, a CBDC that can be treated like a currency such as the yen must be (1) digitized, (2) denominated in a legal currency such as the yen, and (3) issued as a debt of the central bank. , which satisfies the conditions.
The Bank of Japan, which has been considering the feasibility of CBDC for some time, announced in October 2020 its policy on how to approach it. Among them, the following five characteristics are required for CBDC.
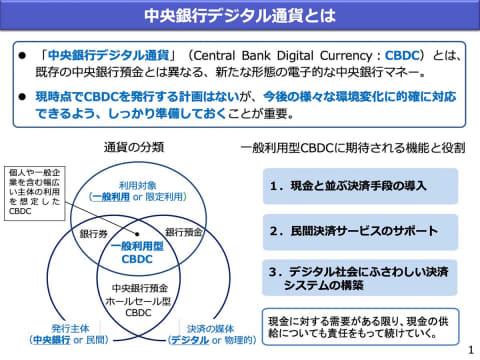
(1) Universal access In order to make it available to anyone, we will not limit the users of the terminals and cards used for remittance and payment, and consider portability.
(2) Prevent fraud, such as making security counterfeiting difficult.
(3) Secure a system that can be used even if there is a failure of the resilient system or communication network, power outage, etc.
(4) Immediate Settlement As with cash, we will be able to complete the settlement process quickly. Moreover, it enables many users to make frequent payments.
(5) Interoperability Ensure interoperability with private payment systems operated by banks and electronic money providers.
Source: Bank of Japan / "The Bank of Japan's Policy on Central Bank Digital Currencies" reference material
Differences from electronic money and crypto assets
Electronic money looks similar to CBDC at first glance, but it is nothing more than data managed by a payment company. Stores that can be used are limited to those that have a contract with the vendor. Basically, it cannot be exchanged for other electronic money, and it is not easy to convert the balance into cash. In addition, stores that receive payment for goods and services in electronic money will have to wait a month or two for cash to be deposited.
On the other hand, CBDC digitizes banknotes, which are "payment and settlement instruments that anyone can use 24 hours a day, 365 days a year" issued by the central bank. You don't have to choose any store to use it, you can send money to anyone, and the delivery will be completed instantly. Plus, there's no need to carry or store bulky bills and coins, and you're freed from manually counting balances.
Then, how is it different from crypto assets realized with blockchain technology? Crypto assets such as Bitcoin are not issued by a central bank and have no guaranteed value. Prices fluctuate so much that it cannot be used for everyday payments.
Because the value of CBDC is exactly the same as legal currency, it does not fluctuate like crypto assets. It can be used for payments in the same way as cash today.
The Bank of Japan is conducting demonstration experiments on CBDC
CBDC is being operated and examined on a trial basis around the world. The Bank of Japan also started a demonstration experiment in April 2021, not just a desk study.
Phase 1 will start in April
The purpose of the experiment is to confirm whether the functions and characteristics required for CBDC are technically feasible. This time, which started in April, it is called a "proof of concept (proof of concept phase 1)", and an experimental system will be built to verify basic functions such as CBDC issuance, remittance, and return. Phase 1 is scheduled to end in March 2022, and in Phase 2, additional functions will be added and verified.
If the need is recognized after the second phase of the demonstration experiment, we may conduct a pilot experiment in which private businesses and consumers participate. In that case, although the region and target audience are limited, you may be able to experience the digital circle as soon as possible.
European Central Bank and Bank of Japan's Project Stellar
A CBDC like the Digital Yen would need to assume cooperation with legal currencies of other countries. Therefore, the Bank of Japan is conducting an initiative called "Project Stella" and is considering it jointly with the European Central Bank.
Project Stellar is investigating Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), which is the foundation of CBDC and others. We are trying to identify the impacts and issues that DLT will have on financial market infrastructures and use them for future discussions. Most recently, in February 2020, the 4th phase research report was published.
Many major countries are cautious about digital currency
Although there are many benefits, it is technically difficult to build a robust CBDC system that can be used stably 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. Nevertheless, it is being considered by countries as it could be a powerful tool to prevent tax evasion and money laundering. However, due to privacy concerns, states will not be allowed to monitor all CBDC transactions. To realize CBDC, it is necessary to solve such legal problems.
For that reason, many major central banks are said to be cautious, except for some, such as China, which is aggressive towards the "digital yuan." The Bank of Japan is only considering it, and has no plans to issue a digital yen at this time.
However, eventually CBDC will be introduced in many currencies. According to the "Deloitte 2021 Global Blockchain Survey" (published on August 19, US time), a survey conducted by Deloitte around the world, 76% of business owners believe that cash will be obsolete in the near future and that digital assets will become less common in the next decade. I thought that legal tender would replace it. Even if you don't have to deal with it right now, it seems that you need to be aware of it.
Salary digital payment, lifting the ban soon? Companies are cautious about introducing the government plans to lift the ban on "digital payment" that allows employees to receive salaries in electronic money accounts by the end of 2021. PayPay...See details Cashless payment expense reimbursement, no need for paper receipts You'll be able to settle your bill...read more